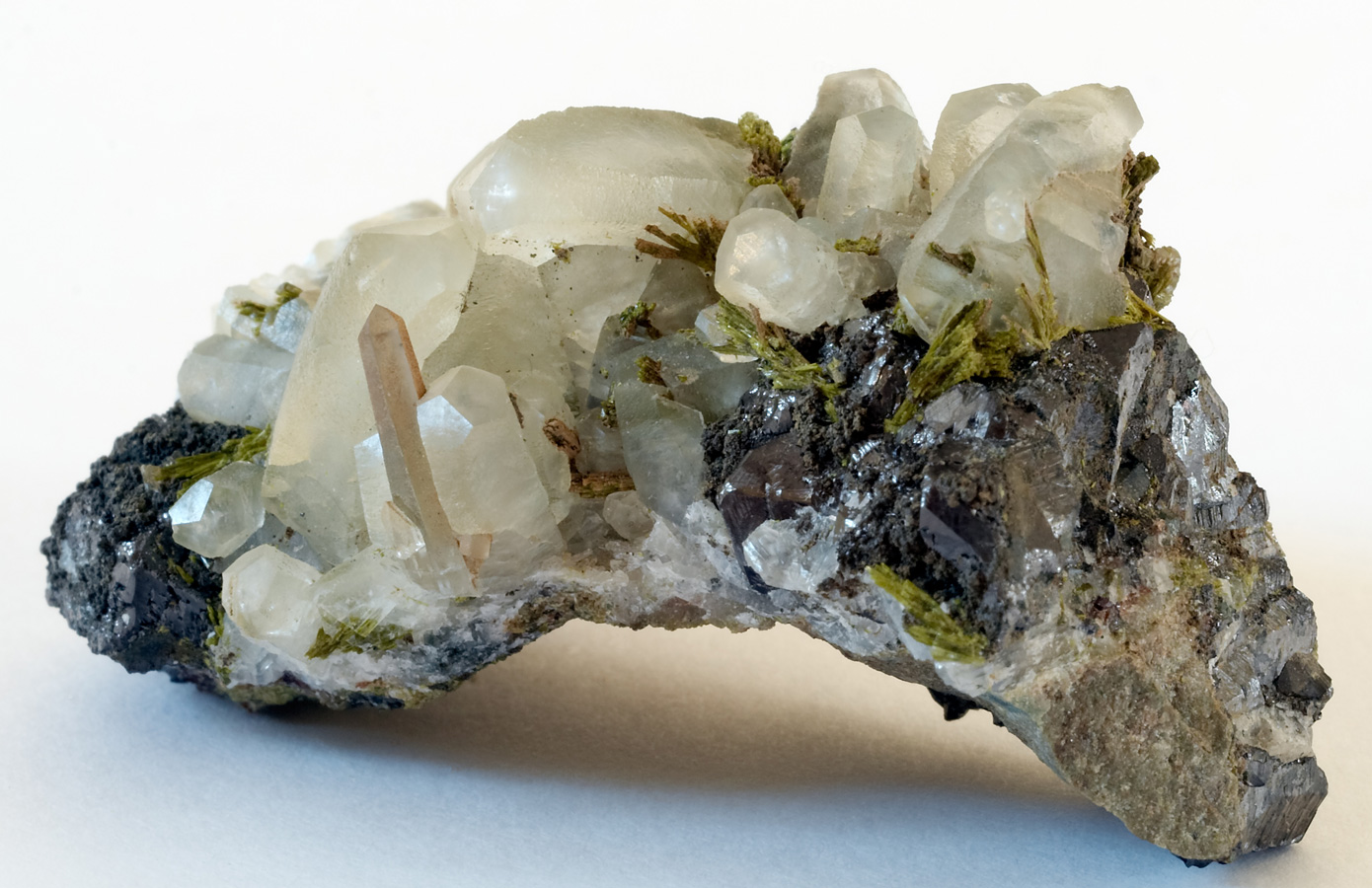
Cause of Color : Iron
Chemical Composition : Calcium Aluminium Silicate with Iron – Ca2(Fe,Al)3(SiO4)3(OH)
Classification / Type : The epidote group is an isomorphous group comprising the following minerals:
- Zoisite
- Clinozoisite
- Epidote
- Piedmontite
- Hancockite
- Allanite
Crystal System / Forms : Monoclinic System / Prismatic crystals with vertical striations.
Cuts & Uses : Facetted, cabochons, etc.
Dispersion : 0.030
Hardness : 6.5
Lustre : Vitreous
Magnification : Parallel needle inclusions, strong doubling of facet edges and inclusions, color zoning.
Optic Character : Anisotropic, D.R.; Biaxial negative (may show pseudo-uniaxial)
Pleochroism : Strong (green, brownish red, yellow)
Refractive Index / Birefringence : 1.729 – 1.768 / 0.019 – 0.045
Simulants (with separation tests) : Tourmaline (R.I., S.G., spectrum), Kornerupine (R.I., S.G., spectrum), Sillimanite (R.I., S.G., spectrum, pleochroism)
Sources : U.S.A., Sri Lanka, India, Myanmar, Madagascar, Austria, Norway, Switzerland.
Specific Tests : The strong reddish brown pleochroic color is often mistaken for a color change phenomena.
Spectrum : 455nm, 475nm (Directional)




























Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.